How to Perform Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises
This page explains how to perform range of motion (ROM) exercises on a patient. Included are pictures that highlight how to perform common passive ROM exercises.
Click here for a poster of these exercises
Why? Types Motions Goal Passive Other Thoughts
Why Perform Them?
Why perform them to begin with? If your patient is on bedrest and isn't active, their muscles can atrophy. Atrophy means their muscle mass decreases because they aren't being used. There is also a decrease in the mobility of joints. This causes issues such as not being able to walk or do basic tasks due to generalized weakness.
The Two Types
The two types of range of motion exercises are active and passive.
Active is when the patient can perform the exercises themselves. They just need assistance on how to do them. It is important to make sure they are doing them correctly and performing enough repetitions.
Passive is when they require assistance to perform the exercises. They may even be totally dependent on you doing the exercises for them.
Types of Motions
There are three different types of motions that are used depending on the extremity and joint.
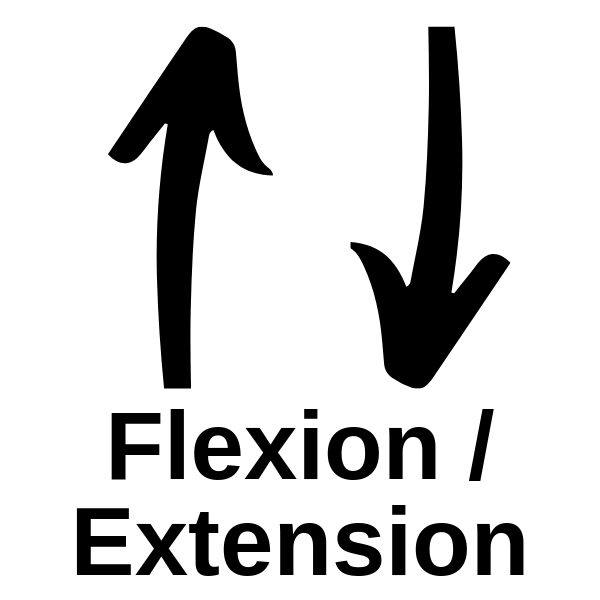
- Flexion and extension is done in an up and down motion.
- Abduction and adduction is done in a side to side motion.
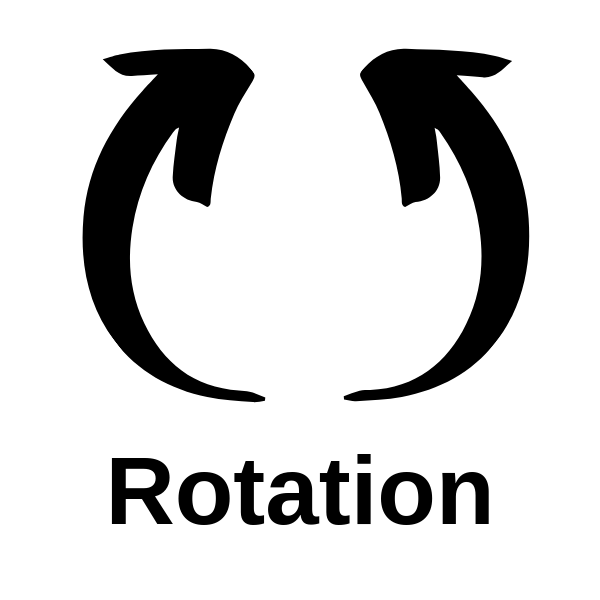
- Rotation is done in a circular motion.

What is the Goal?
What is the goal of these exercises? Does the patient need to regain their strength or simply retain the strength and movement that they already have? If the order is given by physical therapy (PT), they often prescribe exercises to overcome an injury or the effects of a particular illness by regaining function.
More often than not, ROM exercises are done in order to retain the current level of ability in extremities. Therefore, they are usually done on healthy extremities and should not cause pain. If pain is experienced during an exercise, the next repetition should be done below that pain threshold in order to maintain comfort. If pain is experienced, it should be noted and possibly reported depending on the severity. Click here for more about pain management.
Performing Passive Range of Motion Exercises to Major Extremities
Step by Step Instructions
This is a set of step by step instructions based on the clinical skills portion of a CNA exam although they can also be followed in a real world setting. In this particular case, the patient is simply lying in bed and needs passive assistance.
Step 1: Perform your opening duties.
- Knock on the door.
- Introduce yourself.
- Explain your title.
- Identify the patient.
- Describe the skill.
- Obtain permission.
- Close the privacy curtain.
- Perform handwashing.
Step 2: Prepare the patient.
- Raise the entire bed height to a comfortable working position if desired.
- Place the patient supine (flat) in the bed.
- Adjust them towards the center of the bed if necessary.
- Move everything out of the way in order to perform the exercises properly (blanket, bedside table, etc.).
Step 3: Ensure all of these precautions are taken during the exercises.
- Support each joint while performing the exercises by cupping underneath extremities and gently lifting rather than gripping an extremity from above in a claw-like fashion.
- Move all joints slowly and gently without overextending and causing pain. Only move to the point of resistance.
- If pain does occur, perform the next exercise by stopping movement below the pain threshold as to not cause pain again.
- Describe each exercise to the patient immediately before performing them.
- Only perform exercises on sides and joints that are listed in the care plan or physician orders. (example: “left shoulder only” would exclude the right shoulder).
- Repeat exercises only as many times as directed in the care plan (example: three reps).
Step 4: Flexion and extension (up and down motion) of the shoulder.
- Straighten the patient’s arm flush against their side and lay it flat on the bed.
- Cup underneath the patient’s elbow with one hand and cup underneath their wrist with your other hand.
- Raise their arm at the shoulder joint above their head and towards the head of the bed as if they were needing to ask a question.
- Gently lower the arm back down to its original position on the bed.
- Repeat as necessary.
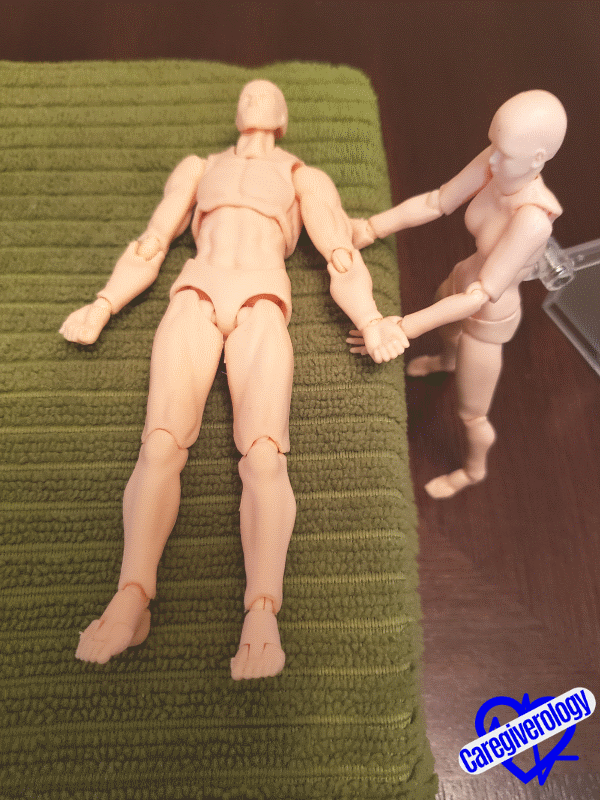 Starting position
Starting position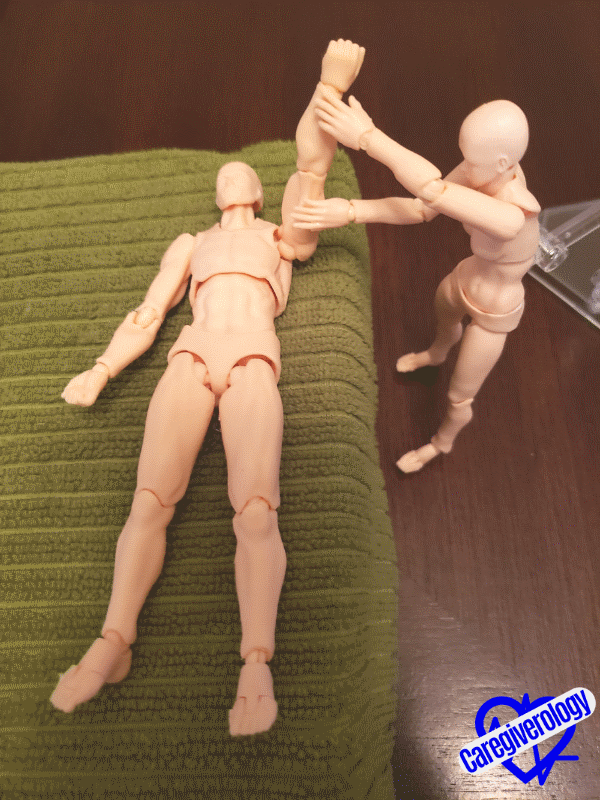 Asking a question
Asking a questionStep 5: Abduction and adduction (side to side motion) of the shoulder.
- Straighten the patient’s arm flush against their side and lay it flat on the bed.
- Cup underneath the patient’s elbow with one hand and cup underneath their wrist with your other hand.
- Move the arm sideways and away from their body at the shoulder joint as if they were making a snow angel.
- Gently move the arm back to its original position on the bed.
- Repeat as necessary.
 Starting position
Starting position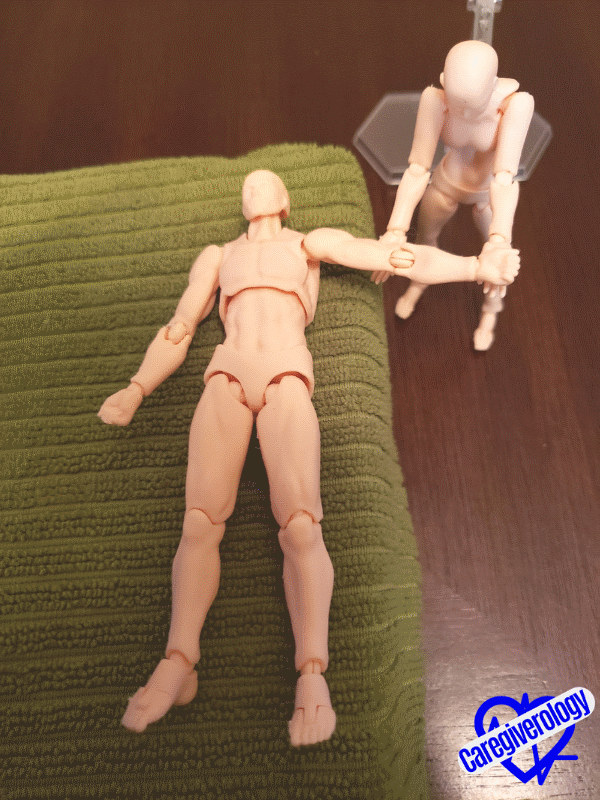 Snow angel
Snow angelStep 6: Flexion and extension (up and down motion) of the elbow.
- Keep the patient’s elbow on the bed with their palm facing up throughout this exercise.
- Straighten the patient’s arm flush against their side and lay it flat on the bed.
- Cup underneath the patient’s wrist with your hand.
- Lift their lower arm straight up and bring it towards their shoulder by bending it at the elbow joint as if they were flexing their bicep muscle.
- Gently move the arm back to its original position on the bed.
- Repeat as necessary.
 Starting position
Starting position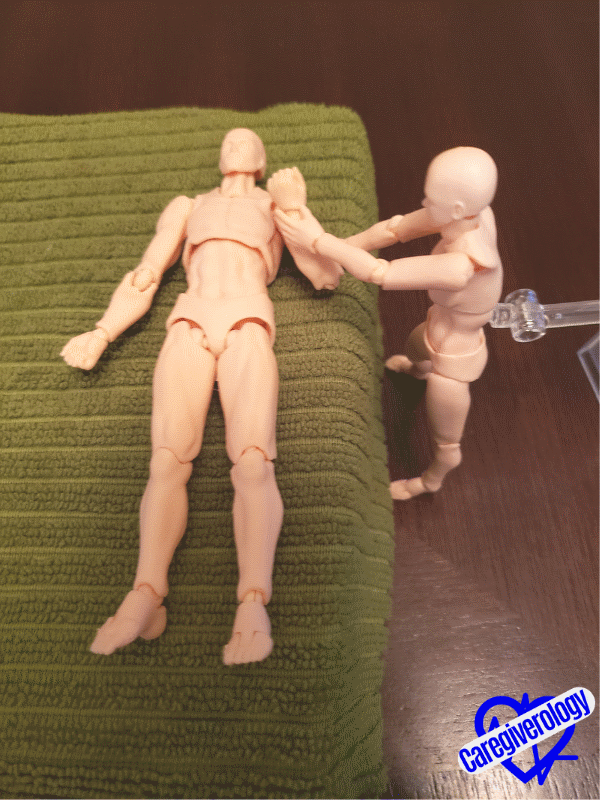 Bicep flex
Bicep flexStep 7: Flexion and Extension (up and down motion) of the wrist.
- Keep the patient’s elbow on the bed with their palm facing up throughout this exercise.
- Straighten the patient’s arm flush against their side and lay it flat on the bed.
- Cup underneath the patient’s forearm with one hand.
- Lift their lower arm straight up by bending it at the elbow joint.
- With your other hand, curl their fingers into a fist and gently grip their fist.
- Bend their fist forward to the point of resistance without causing pain as if they were knocking on a door.
- Then bend their fist backwards to the point of resistance without causing pain as if they were twisting the throttle of a motorcycle.
- Return the fist back to its original position.
- Repeat as necessary.
- After all of the reps are done, gently place the patient’s lower arm back onto the bed.
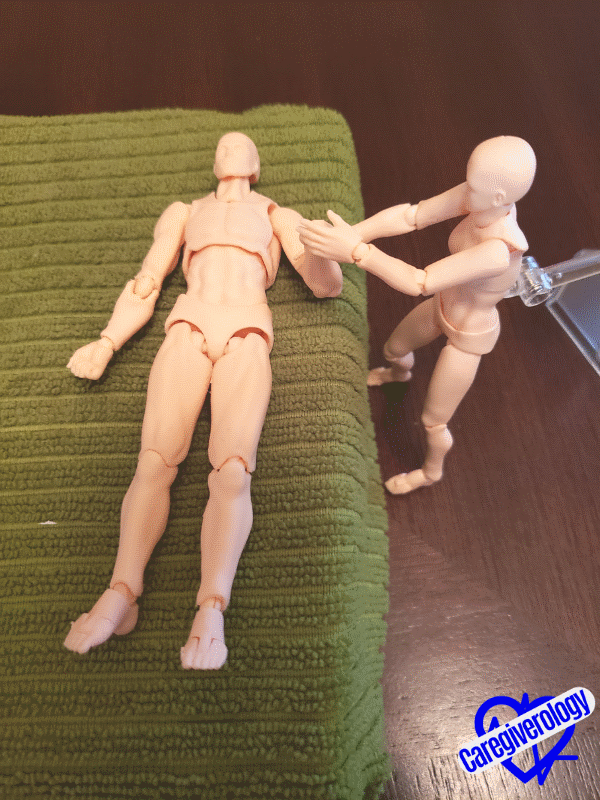 Knocking on a door
Knocking on a door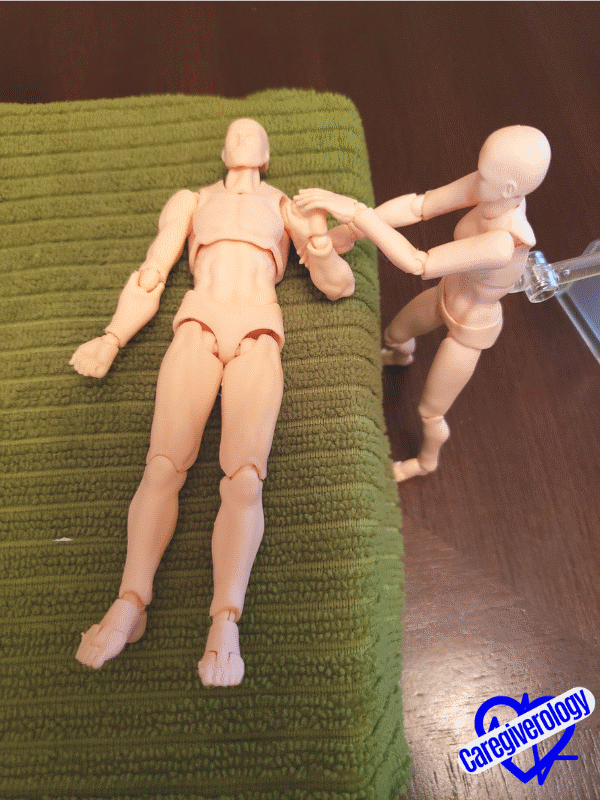 Revving a motorcycle
Revving a motorcycleStep 8: Flexion and extension (up and down motion) of the hip and knee.
- Straighten the patient’s leg flush against the bed.
- Cup underneath their knee with one hand.
- Cup underneath their ankle with your other hand.
- Lift their thigh (upper leg) up from the bed by bending at the hip joint while simultaneously keeping the calf (lower leg) straight by bending at the knee joint. This motion should bring their knee towards their chest as if they were climbing up a step.
- Return the leg back to its original position.
- Repeat as necessary.
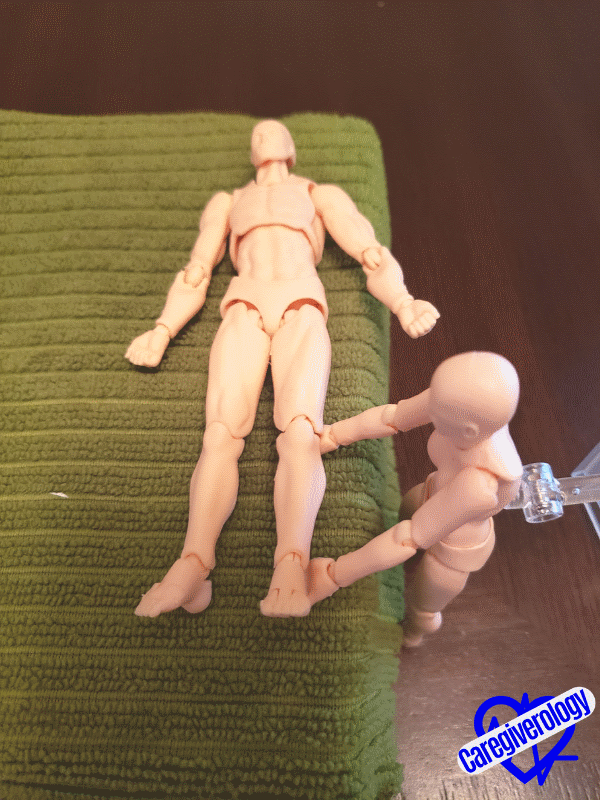 Starting position
Starting position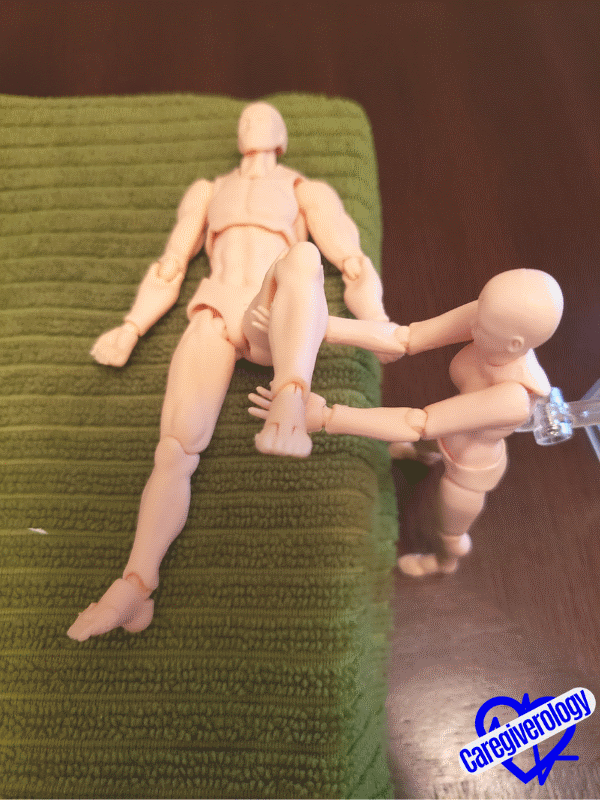 Climbing a step
Climbing a stepStep 9: Flexion and extension (up and down motion) of the ankle.
- Straighten the patient’s leg flush against the bed.
- Cup underneath their calf (lower leg) with one hand.
- Raise the leg up slightly off of the bed.
- Gently grasp the top of their foot with your other hand.
- Bend their foot forward and down towards the bed at the ankle joint as if they were pushing on a gas pedal.
- Then bend their foot backwards at the ankle joint bringing their toes up towards their knee.
- Return the foot back to its original position
- Repeat as necessary.
- After all of the reps are done, gently place the patient’s leg back onto the bed.
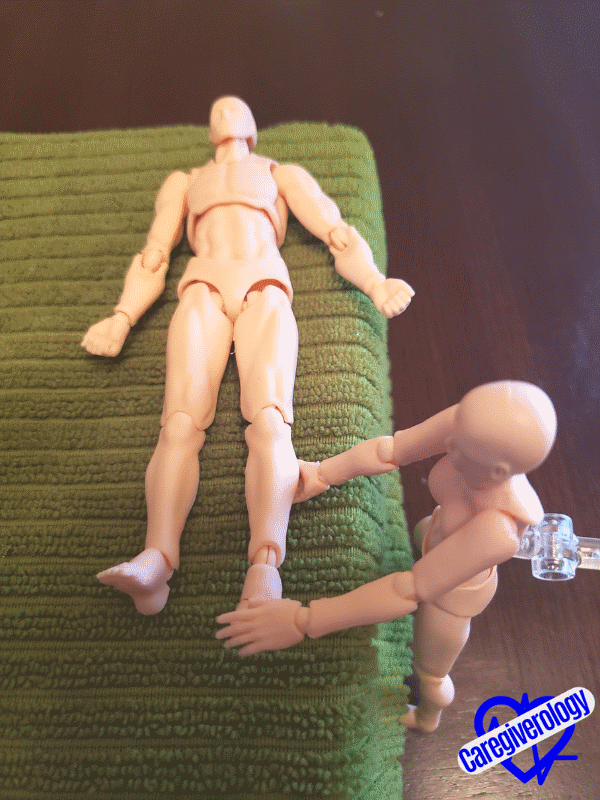 Pushing on a gas pedal
Pushing on a gas pedal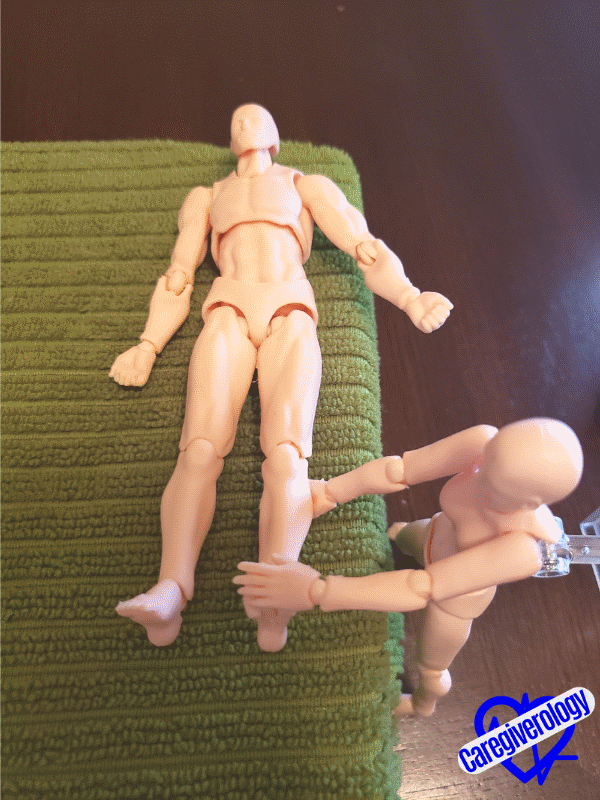 Toes up towards the knee
Toes up towards the kneeStep 10: Perform your closing duties.
- Place the call bell either in the bed with the patient or within their reach.
- Adjust the head of the bed if desired.
- Keep the entire bed height in the lowest position.
- Make sure the bed alarm is on if necessary.
- Open the privacy curtain if desired.
- Ask the patient if they are comfortable and if they need anything else before you go.
- Check to make sure everything is clean and in its proper place.
- Adjust the lights if needed.
- Ask about the door being left open or closed.
- Perform hand hygiene.
Other ROM Exercises
Hip Abduction and Adduction
With one hand, cup underneath the patient's ankle and with your other hand, cup underneath their knee. While keeping the knee straight, move the leg towards you to about a 45 degree angle if the patient can tolerate it. Then bring the leg back to it's original position. This should look similar to making a snow angel.
 Starting position
Starting position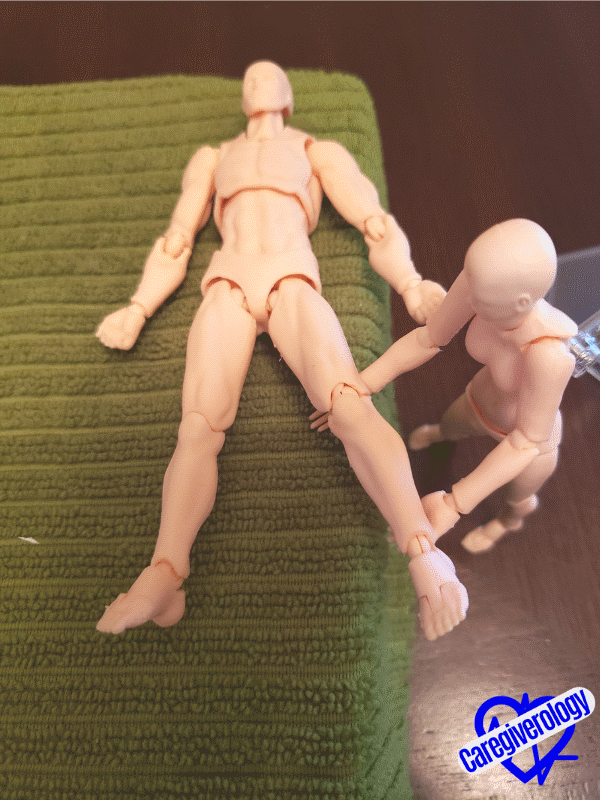 Snow angel
Snow angelNeck Rotation, Flexion, and Extension
Rotation (side to side): With one hand, support the patient's neck. With your other hand, gently turn the neck from side to side.
Flexion (up and down sideways): With one arm and forearm, support the neck. With your other hand, gently tilt the head down to one side. This should bring the ear down closer to the shoulder.
Extension (up and down straight): Bow the head straight down toward the chest and then return it back to a comfortable position.
Hand and Wrist Flexion and Extension
Wrist Flexion: While gently grasping the wrist in one hand, use your other hand to rock the hand side to side as if the patient were trying to wave at someone.
Finger flexion and extension: While gently grasping the wrist in one hand, use your other hand to curl the patient's fingers into a fist and then straightening them out.
Spread the patient's fingers out and tilt each finger individually side to side.
Bring the thumb over the palm and towards the pinky.
Touch the tip of each finger to the thumb.
Final Thoughts
It is important to note that there are many more range of motion exercises that a patient can perform. This is just a summary of some of the most common ones. Again, I want to emphasize to have a clear order from physical therapy of all of the exercises the patient needs and be sure not to cause pain while performing them.
If you have any questions or if there are exercises you are unclear about or ones that are not listed here, please let me know in the comments down below.
What are the Duties of a Caregiver?
Medical References and Resources for Caregivers
From How to Perform Range of Motion (ROM) Exercises to Home
References:
https://alsworldwide.org/assets/misc/RANGE_OF_MOTION_EXERCISES_WITH_PHOTOS_copy.pdf
https://www.drugs.com/cg/active-range-of-motion-exercises.html
Recent Articles
-
Common Truck Crash Injuries and Legal Remedies - Caregiverology
Jul 19, 25 10:49 AM
Known for its sun-drenched beaches, vibrant arts scene, and bustling maritime industry, Fort Lauderdale is a city that sees heavy traffic both on its roads and at its busy port. Unfortunately, with th… -
Why Expert Legal Help Matters After Serious Injury - Caregiverology
Jul 19, 25 10:35 AM
In Houston, over 67,600 car crashes occurred in 2023, resulting in 290 fatalities and 1,612 serious injuries. That’s roughly 185 accidents every day. -
How Life Care Planners Support Injury Recovery - Caregiverology
Jul 19, 25 10:18 AM
In Los Angeles, life care planners play a vital role in supporting injury recovery, especially for individuals facing catastrophic injuries such as traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord damage.





New! Comments
Have something to say about what you just read? Leave a comment in the box below.