How to Check a Body Temperature
 Thermometer
ThermometerThe most common method of taking a body temperature is orally with a thermometer. Other methods include rectally and axillary (in the armpit). The average temperature is considered 98.6 F.
How often should you check your patient's temperature? Working as a nurse, my patients get checked every 4 hours along with the rest of their vital signs, which is the standard for most hospitals. The amount of times you check your patients temp may vary greatly depending on their condition.
A good mindset is when in doubt, check it. Especially if they are disoriented or elderly. The older people get, the harder it is for them to tell if their temp is out of the ordinary. It also becomes more dangerous.
While the average oral temperature is 98.6, anything other than that is not automatically "bad". Our temps actually fluctuate throughout the day and night. The lowest occurring two hours before a person gets up and highest during physical activity.
Thermometers Oral Rectal Axillary Fever Pin
Thermometers
Thermometers come in all different shapes and sizes but they should all give you the same reading. Most nowadays work within a few seconds while older ones may take a minute or two before you get a reading. You can pick one up just about anywhere. They normally have a thin point which is where the temp will be taken.
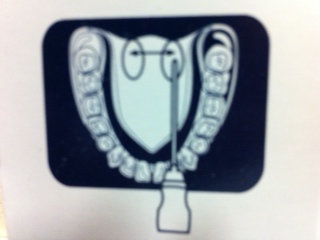 Probe placement
Probe placementOral Temperature
Orally, the thin point goes underneath the tongue as far back in the mouth as possible, without pain or injury of course. Slightly to one side is preferred for the most accurate reading since it can be pushed back deeper. The tongue should lay as flat as possible on the bottom of the mouth so the thermometer is "sandwiched" in between. The mouth should also be closed. The thin point should remain in that very spot until the temperature is taken and readable, usually signified by a beeping sound.
It sounds simple enough, but depending on the patient, it can be a challenging task to get it just right. Make sure they haven't eaten or drunk anything within the last 10 to 15 minutes. If something doesn't seem right or you feel the patient doesn't understand what you are trying to do, talk them through it and make sure they take action. If they still seem to not be adjusting correctly, there are other ways such as...
 Thermometer with probe out
Thermometer with probe outRectal Temperature
Rectally is done of course in the rectum and should read slightly higher than the oral temperature by about one degree. If the patient is alert, definitely warn them before inserting. They don't need to be surprised. The tip of the thermometer should be inside the rectum no more than an inch. Of course, in my opinion along with many others I'm sure, a rectal and oral thermometer should be two separate ones.
Axillary Temperature
Axillary, while not being the best method, is an option as well. The temperature will normally be about one degree lower than the oral method. It should be taken with the tip of the thermometer as close to the center of the armpit as possible. After it is firmly in place, make sure your patient's arm is closed tightly to their side "sandwiching" it.
Fever
A fever is subjective and different for everybody but I personally suggest reporting a temperature of 99.5 F or higher to the patient's nurse. Although that is a low grade fever, depending on the situation, it may be best just to monitor it more often and if it gets any higher, then a fever reducer (tylenol, ibuprofen, etc.) needs to be taken or use of an incentive spirometer might be recommended.
A temperature of 104.0 F or above is considered hyperthermia and needs immediate medical attention. A temperature of 95.0 F or lower is considered hypothermia and also needs immediate medical attention. You should never wait for a temp to go this far. It is best to take action way before.
Pin this page!
List of Caregiver Supplies and Equipment
From How to Check a Body Temperature to Home
Recent Articles
-
Common Truck Crash Injuries and Legal Remedies - Caregiverology
Jul 19, 25 10:49 AM
Known for its sun-drenched beaches, vibrant arts scene, and bustling maritime industry, Fort Lauderdale is a city that sees heavy traffic both on its roads and at its busy port. Unfortunately, with th… -
Why Expert Legal Help Matters After Serious Injury - Caregiverology
Jul 19, 25 10:35 AM
In Houston, over 67,600 car crashes occurred in 2023, resulting in 290 fatalities and 1,612 serious injuries. That’s roughly 185 accidents every day. -
How Life Care Planners Support Injury Recovery - Caregiverology
Jul 19, 25 10:18 AM
In Los Angeles, life care planners play a vital role in supporting injury recovery, especially for individuals facing catastrophic injuries such as traumatic brain injuries or spinal cord damage.




New! Comments
Have something to say about what you just read? Leave a comment in the box below.